When we’re discussing vRAN and Open RAN topics, we’ll find ourselves facing some questions about the performance and cost. The highly common question is ” Can virtualized RAN deliver the […]


RAN (Radio Access Network) is the main telecommunication network component that is located between the core network and users’ equipment (such as a mobile phone). RAN is constituted of a […]
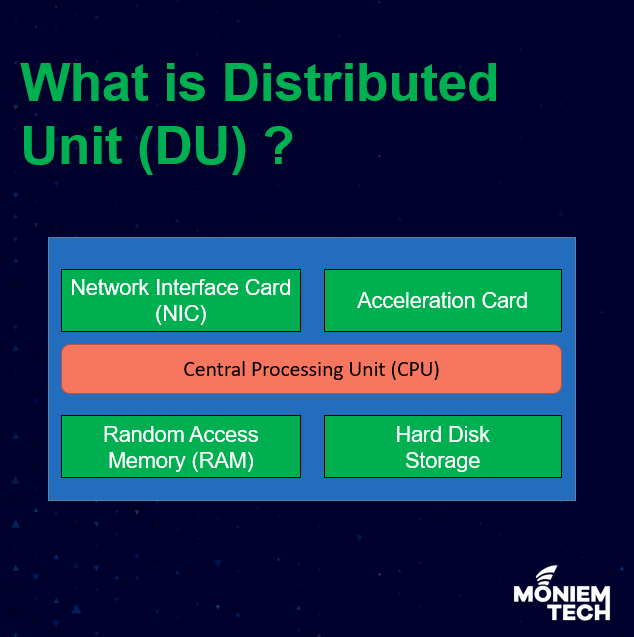
3GPP defined a new RAN architectural in Release 15, where the gNB (Site Name for 5G) is logically split into three entities denoted as: CU: Centralized Unit. DU: Distributed Unit. […]
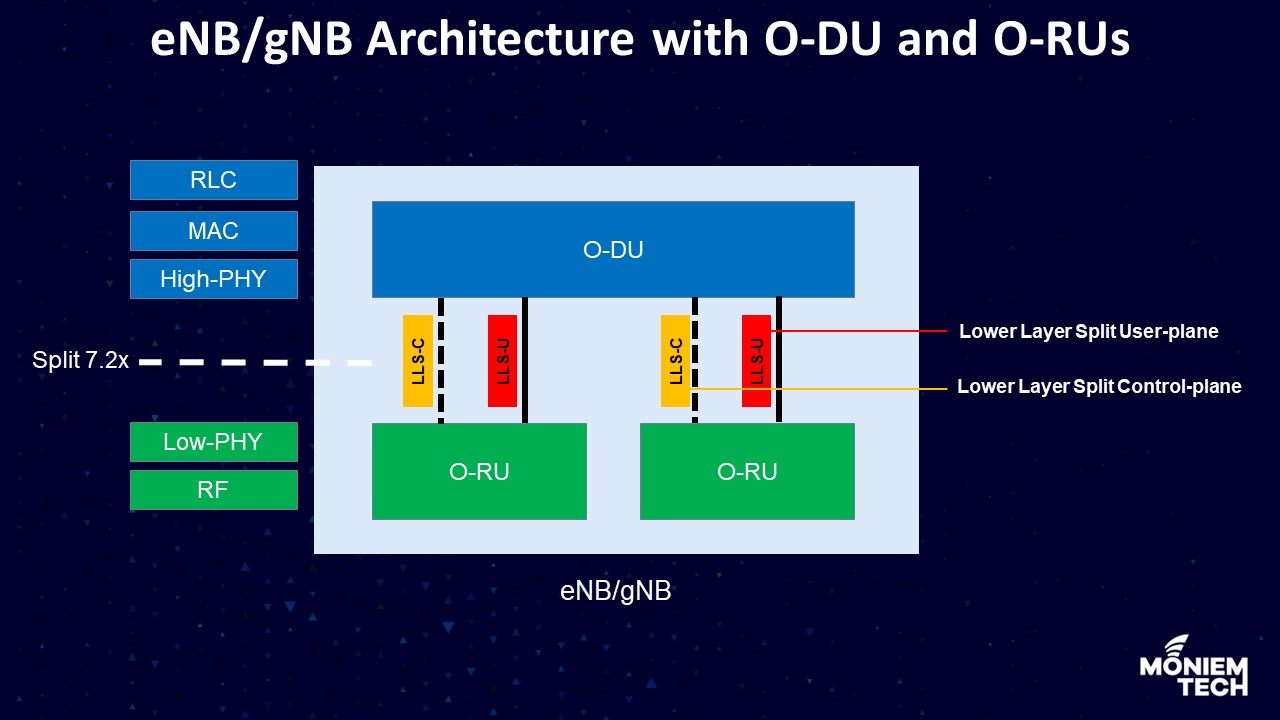
The architecture of eNB or gNB with O-DU and O-RUs has some important definitions here: O-DU: O-RAN Distributed Unit: a logical node hosting RLC/MAC/High-PHY layers based on a lower layer […]
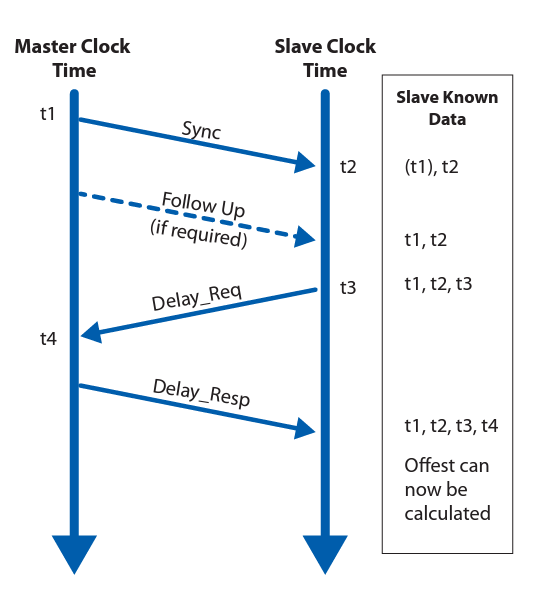
What is PTP? Precision Time Protocol (PTP), defined in the IEEE1588-2008 standard, is a protocol that uses a master-slave hierarchy to synchronize clocks on network devices. PTP uses hardware time […]
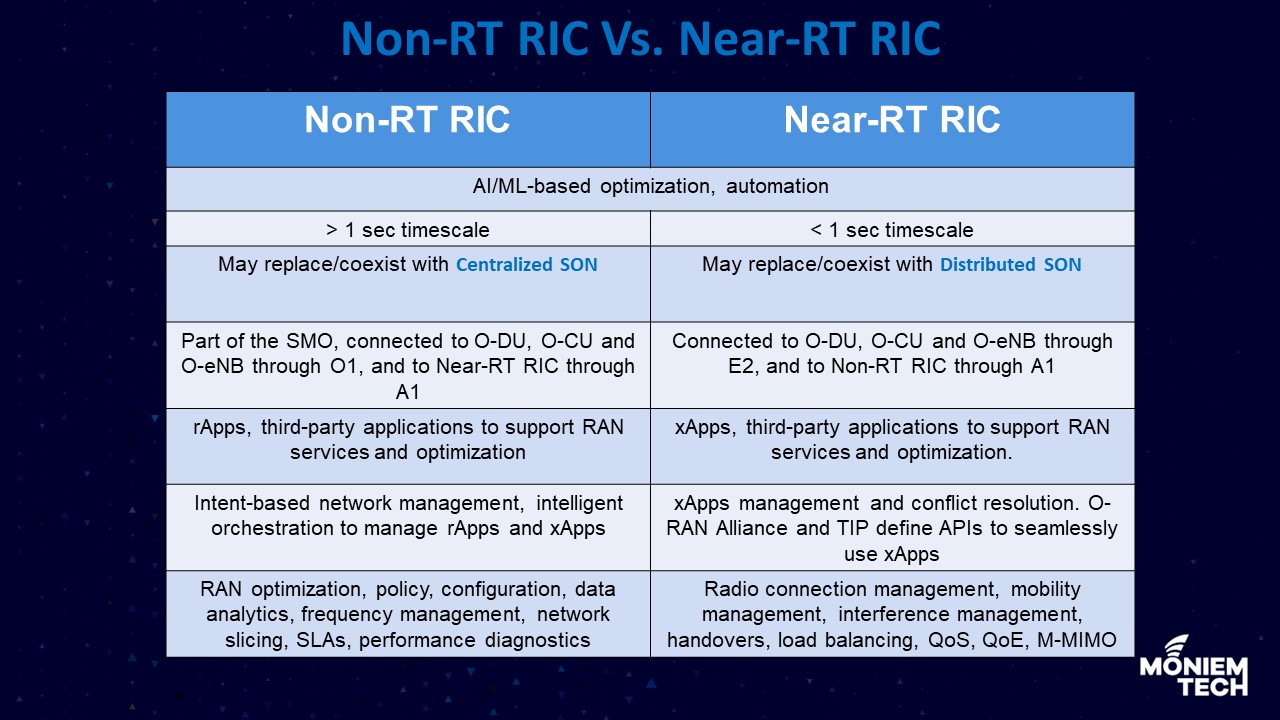
The RAN intelligent Controller (RIC) is cloud-native, and a central component of an open and virtualized RAN network. The RIC aligns with 3GPP release 15 and beyond. It is foundational […]
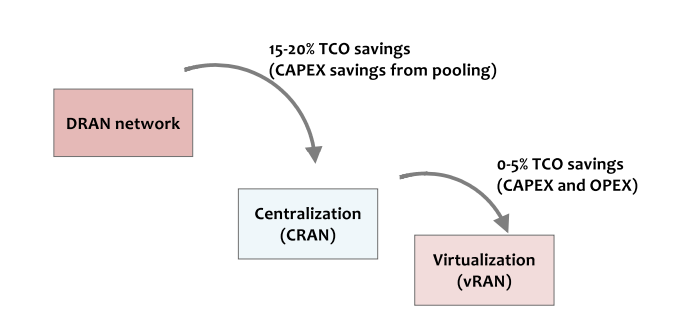
Virtualized radio access networks (vRANs) are a way for telecommunications operators to run their baseband functions as software. One of the primary benefits of virtualizing radio access networks (RANs) is […]
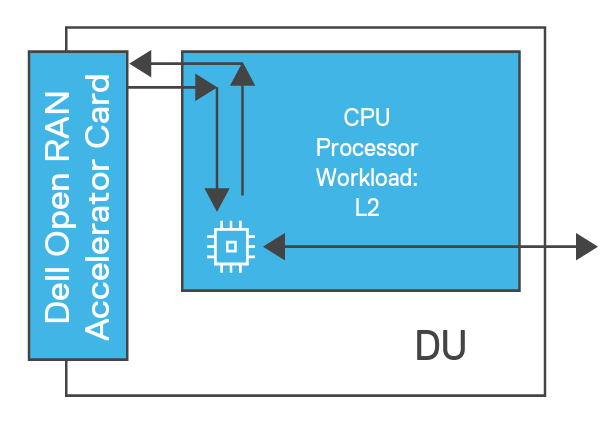
OpenRAN based on legacy compute architectures utilizes an excessively high number of CPU cores and energy to support 5G Layer 1 (L1) and other data-centric processing, like security, networking, and […]
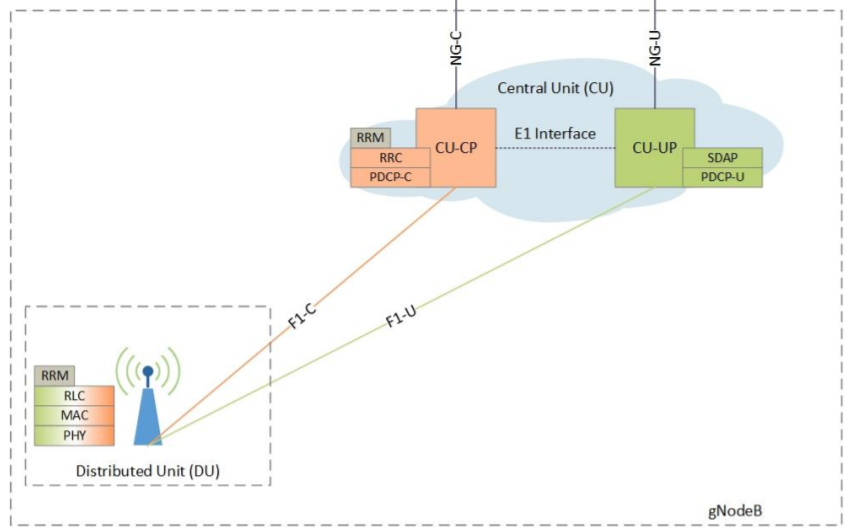
Open RAN disaggregates the RAN into main 3 components as below: ? Upper Layer Split Central Unit (CU) • Logical node that includes a portion of the eNB/gNB functions as defined […]
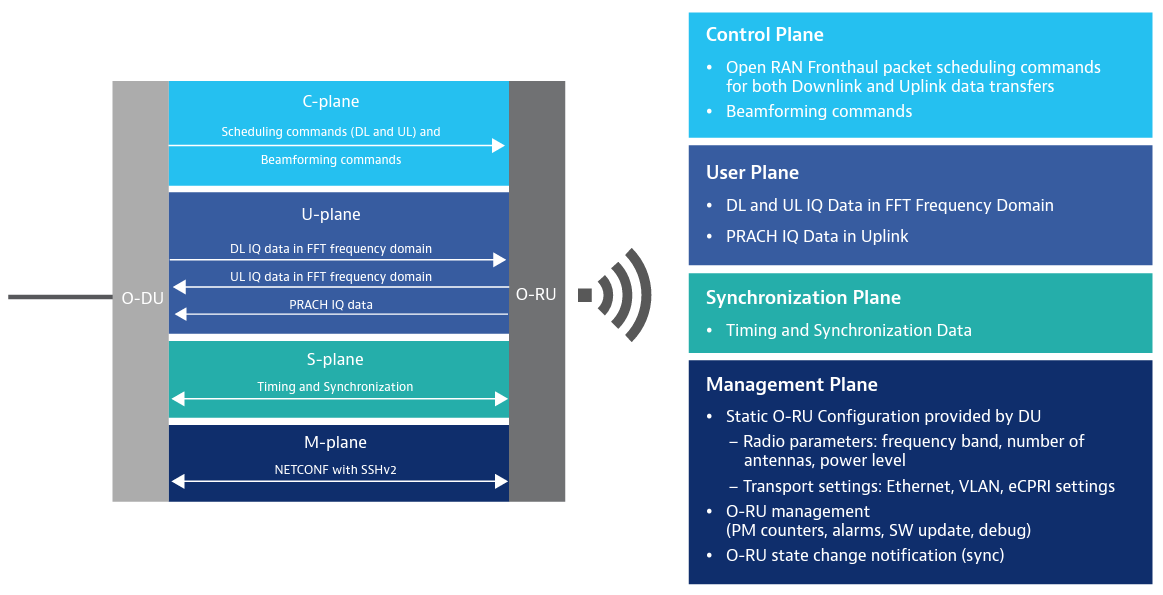
O-RAN’s proposed concepts and architectures use a split-RAN concept. There are 8 known ways to functionally split the RAN, and each one proposes splitting the processing so that different parts […]

