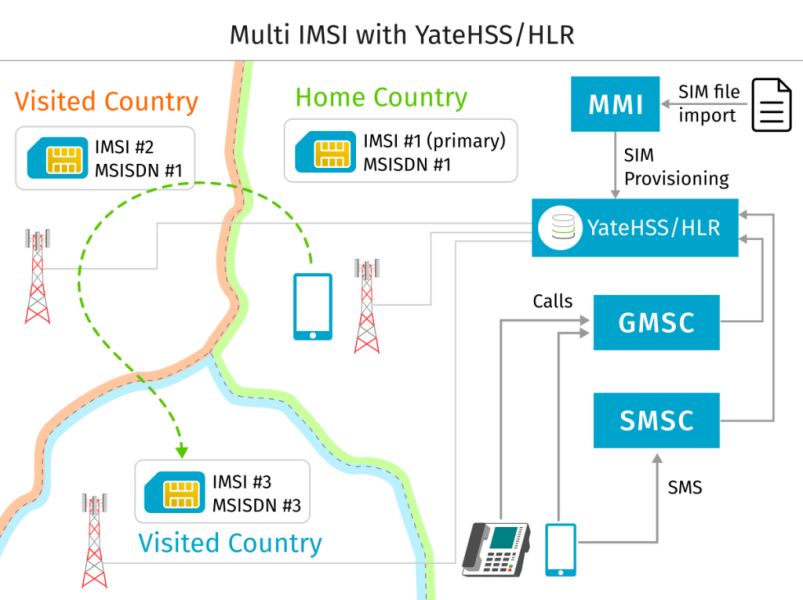
At a conceptual level, the SIM identifies the subscriber to the network and enables this identity to be securely authenticated. When a device connects to a network, the SIM in the device […]
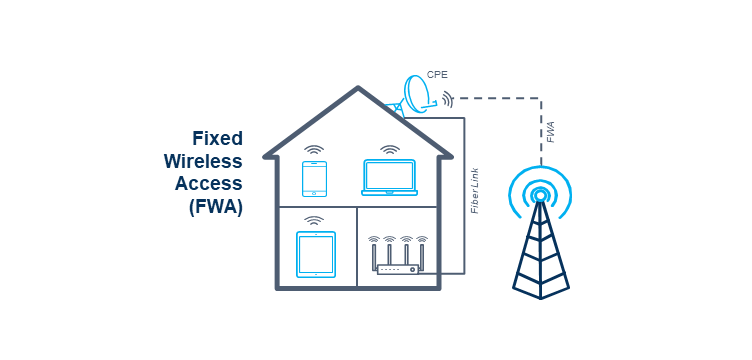
5G has made it possible for wireless networks to compete against fiber, satellite, xDSL, and cable in delivering high-speed broadband service to residences and businesses at attractive prices through FWA. What is FWA? […]
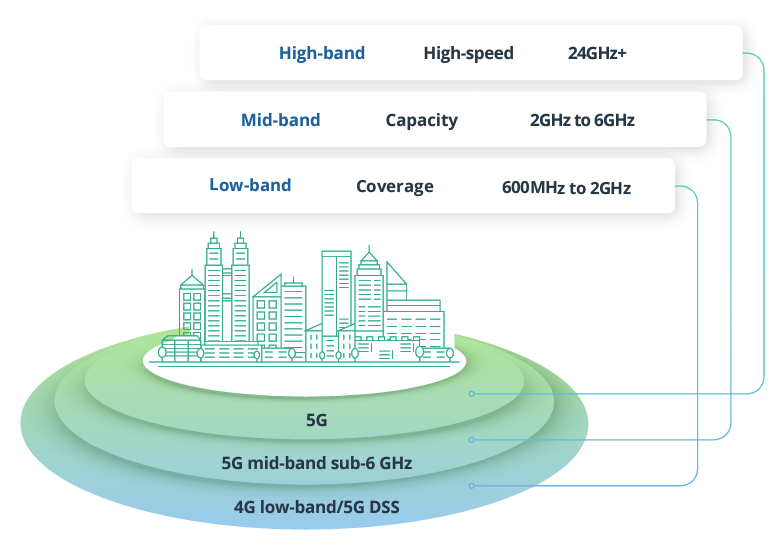
5G defines the use of wide radio channels. Whereas 4G is limited to a maximum radio channel size of 20 MHz, 5G standards specify the use of radio channels up […]
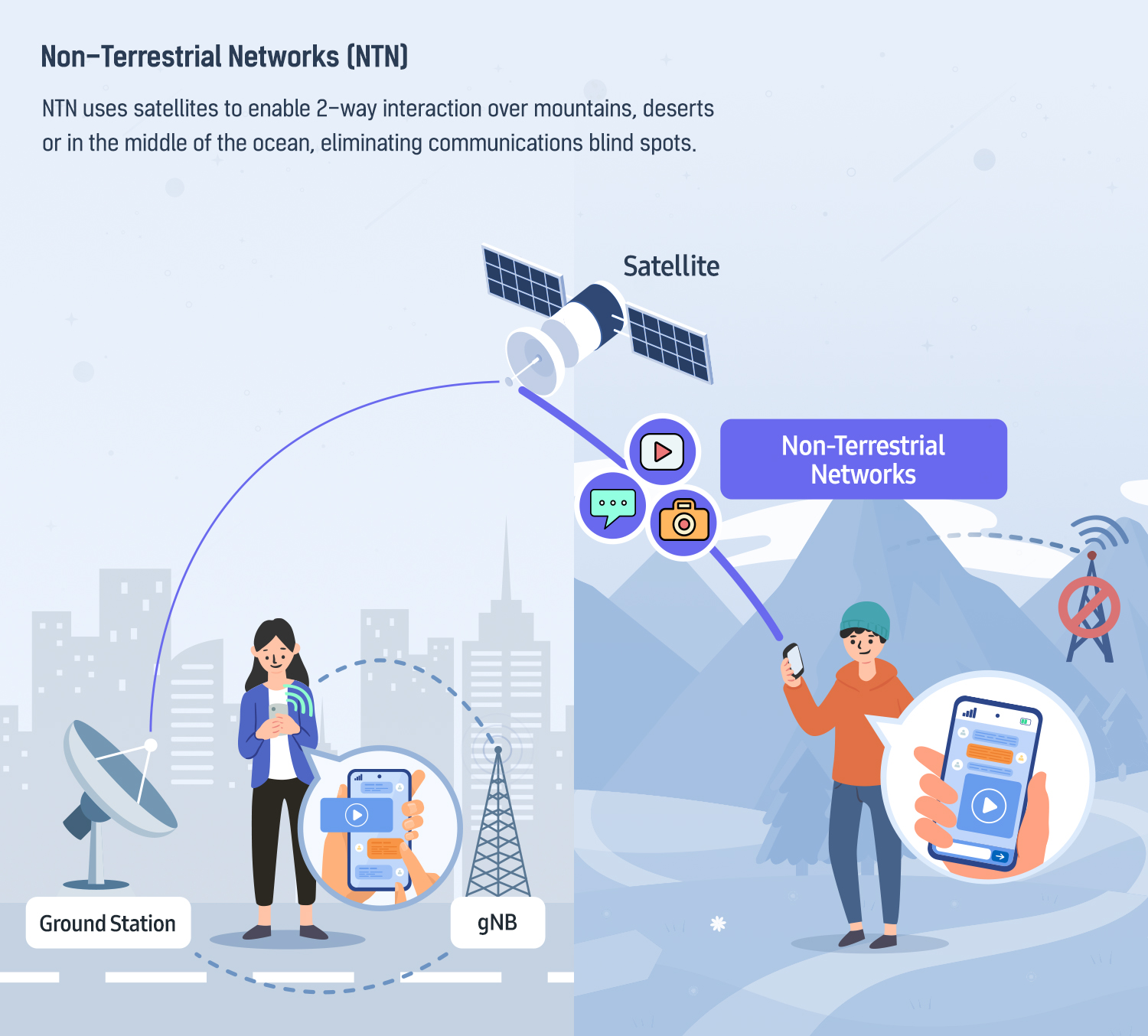
From the perspective of global network coverage, more than 80% of land areas and 95% of sea areas are not covered by ground cellular networks. The 5G network was built […]
5G delivers higher data speeds, and lower latency, and supports more users, devices, and services while simultaneously improving network efficiency. As defined by the Third-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), the 5G […]
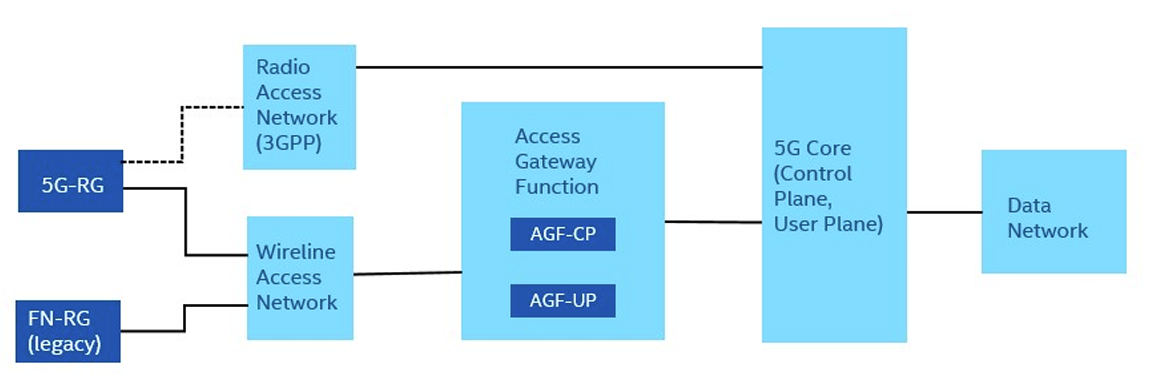
? 5G network comprises a remote radio unit (RRU), distributed unit (DU), a centralized unit (CU), and a core network. The terms fronthaul, midhaul, and backhaul are describing the 5G […]
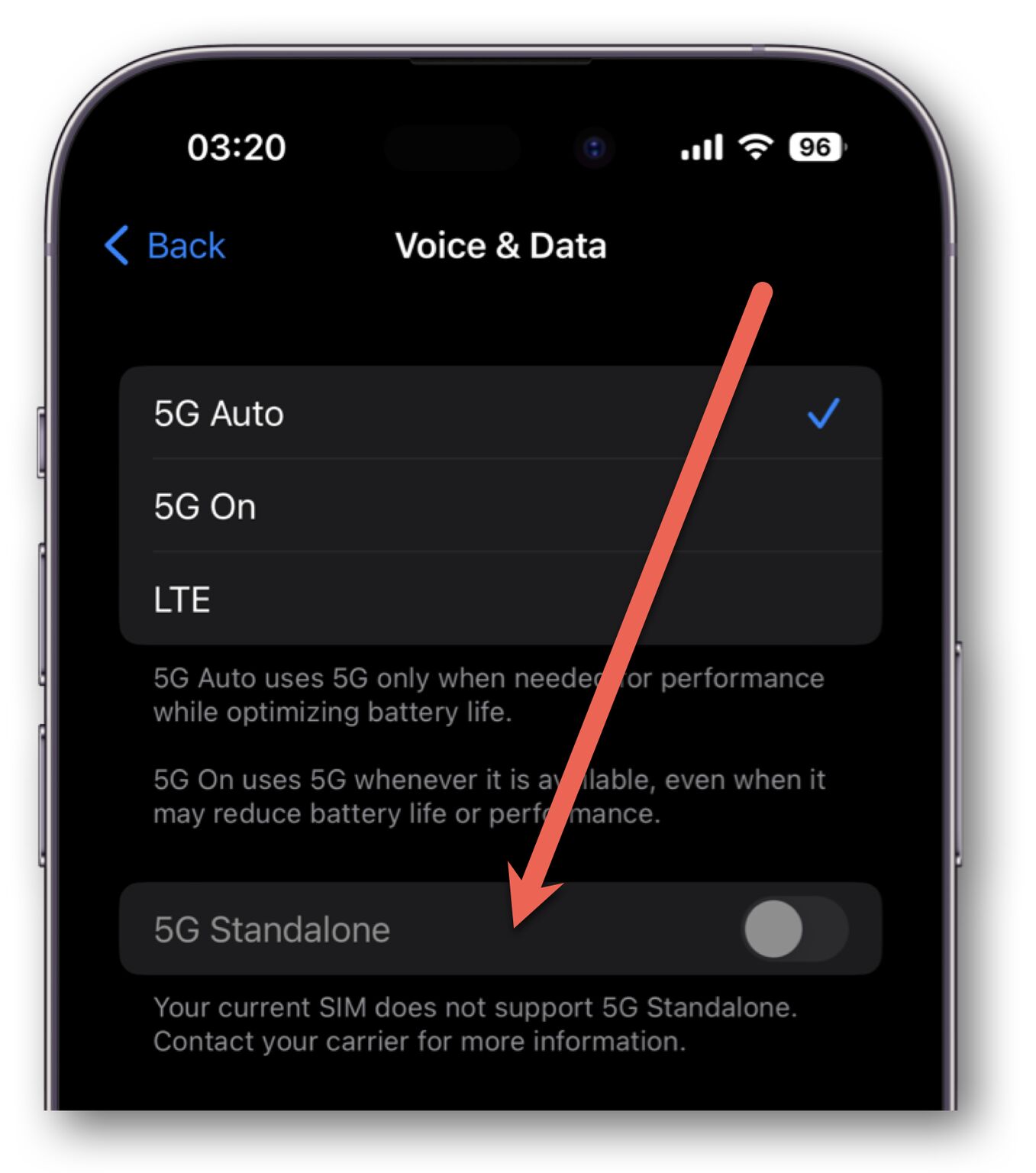
? In 5G SA, NR will enable the service provisioning through gNB (gNodeB) which connects to the new core 5GC (5G Core Network) using NG Interface. ? According to GSMA, by […]
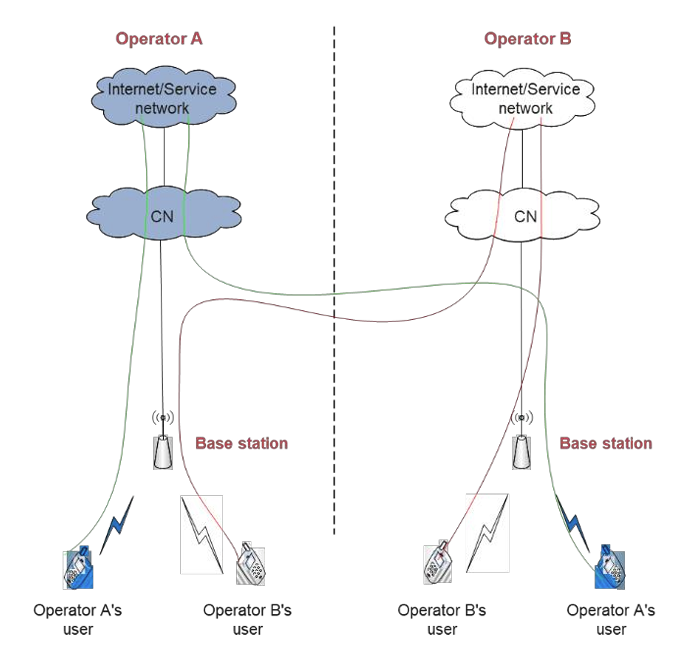
Mobile communication network sharing refers to the sharing of infrastructure or communication equipment among multiple operators. The infrastructure includes towers, buildings, and equipment rooms used for deploying base stations, whilst […]

When we’re discussing vRAN and Open RAN topics, we’ll find ourselves facing some questions about the performance and cost. The highly common question is ” Can virtualized RAN deliver the […]
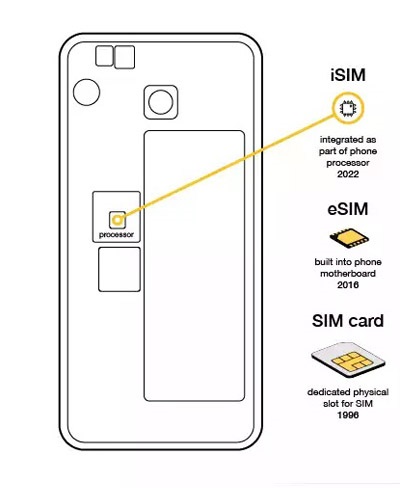
SIM (Subscriber Identity Module) is a reliable method of identifying users, checking the authenticity of endpoint devices, and securing their data. ? Over the years, SIMs have shrunk from the […]
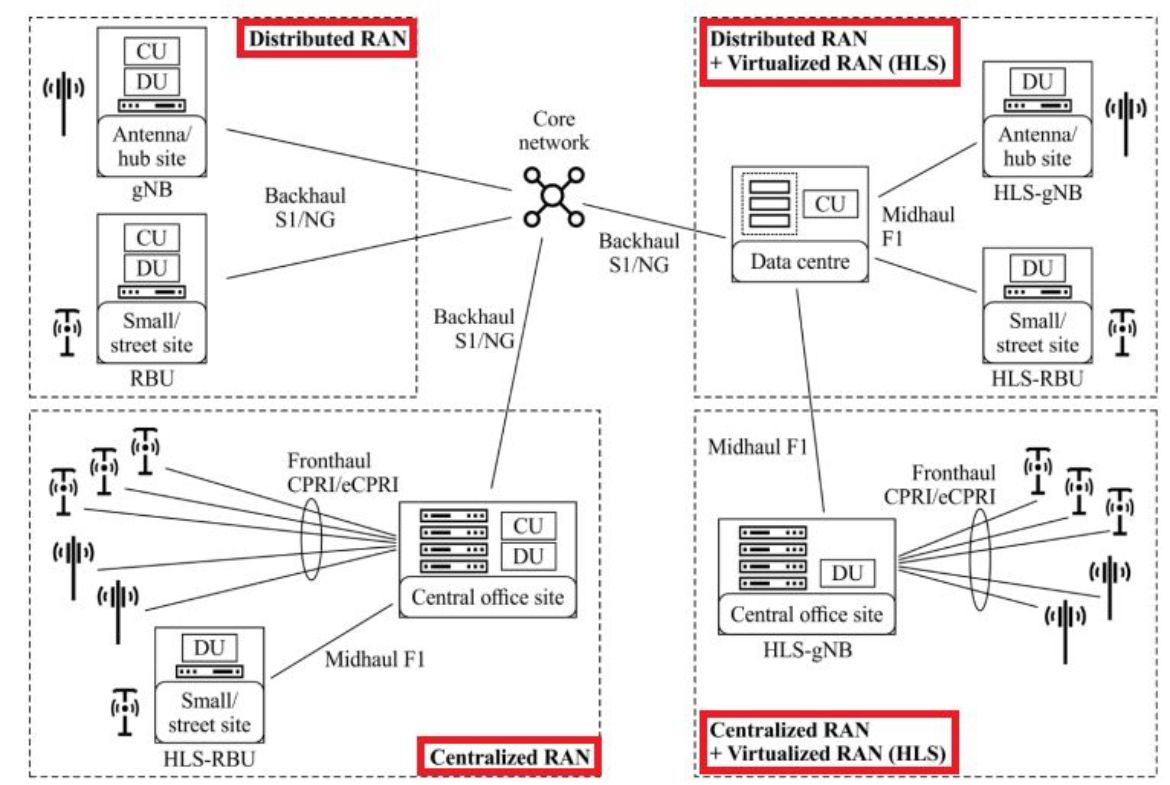
As we know that RAN, Radio Access Network, is divided into two main components: -> Baseband Unit (BBU). -> Radio Unit (RU). The move from D-RAN to C-RAN then v-RAN […]
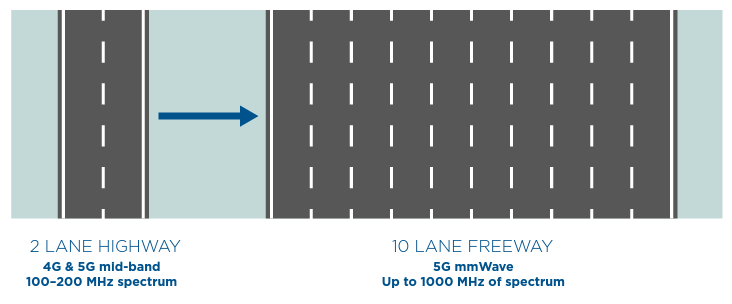
All notes you should know about 5G mmWave Band. ? 5G mmWave refers to the higher range of radio frequencies (above about 24 GHz) supported by 5G. Also, it’s called […]

SMS, Short Message Service, is a secure system that helps protect your customers’ and employees’ data and allows you to contact all users who have a mobile phone. ? In […]
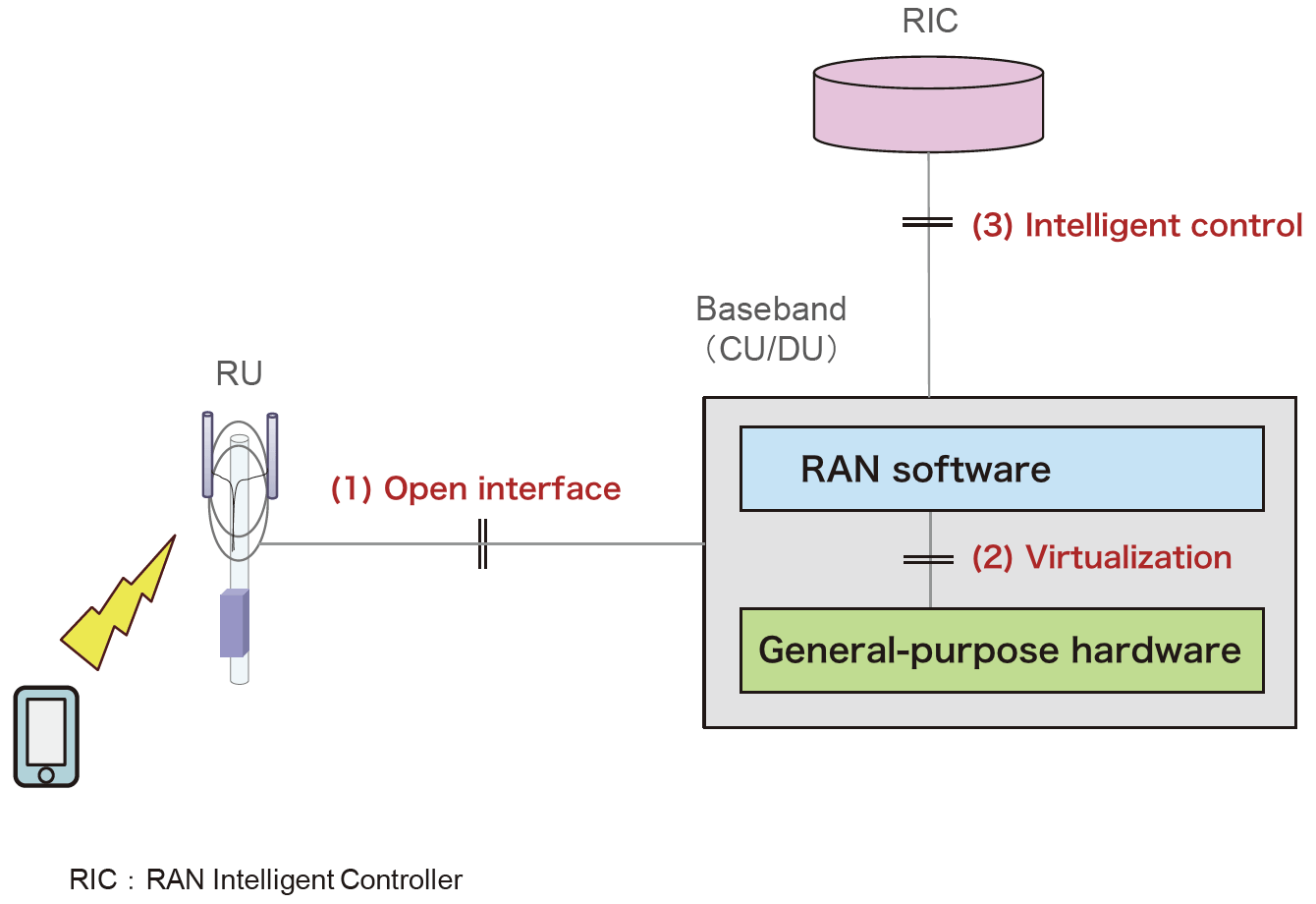
The open radio access network or Open RAN can be broadly divided into the following three elements: Open interfaces that combine RAN equipment from a variety of vendors. Virtualization (i.e., […]

3GPP consists of three Technical Specifications Groups (TSGs) where TSG RAN (Radio Access Network) is responsible for the definition of functions, requirements, and interfaces of the Radio Access. TSG RAN […]
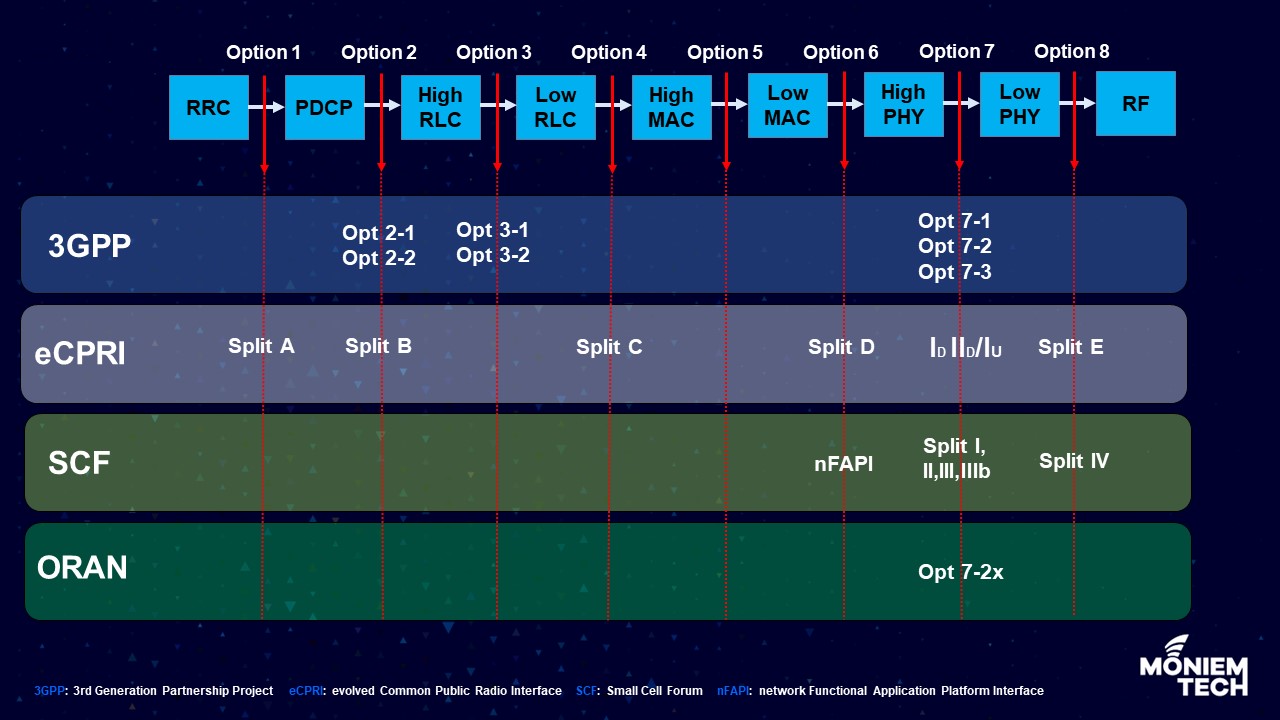
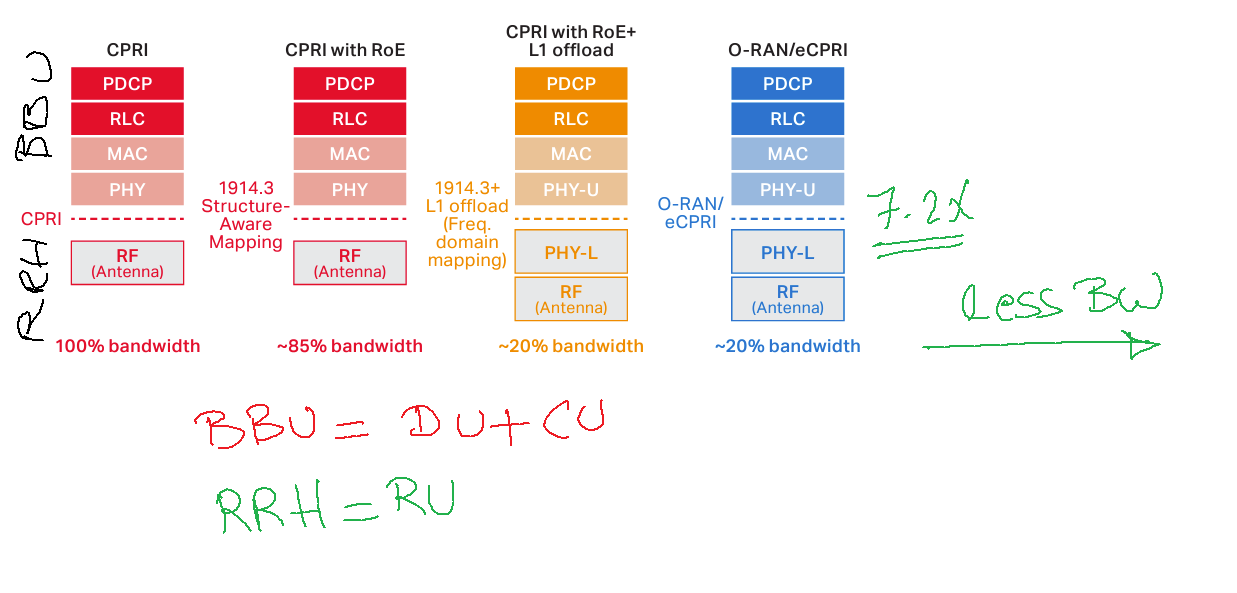
The increase in data rates in 5G makes it impractical to continue with the conventional CPRI fronthaul implementation. Moving towards a higher layer split would relax the latency and bandwidth […]
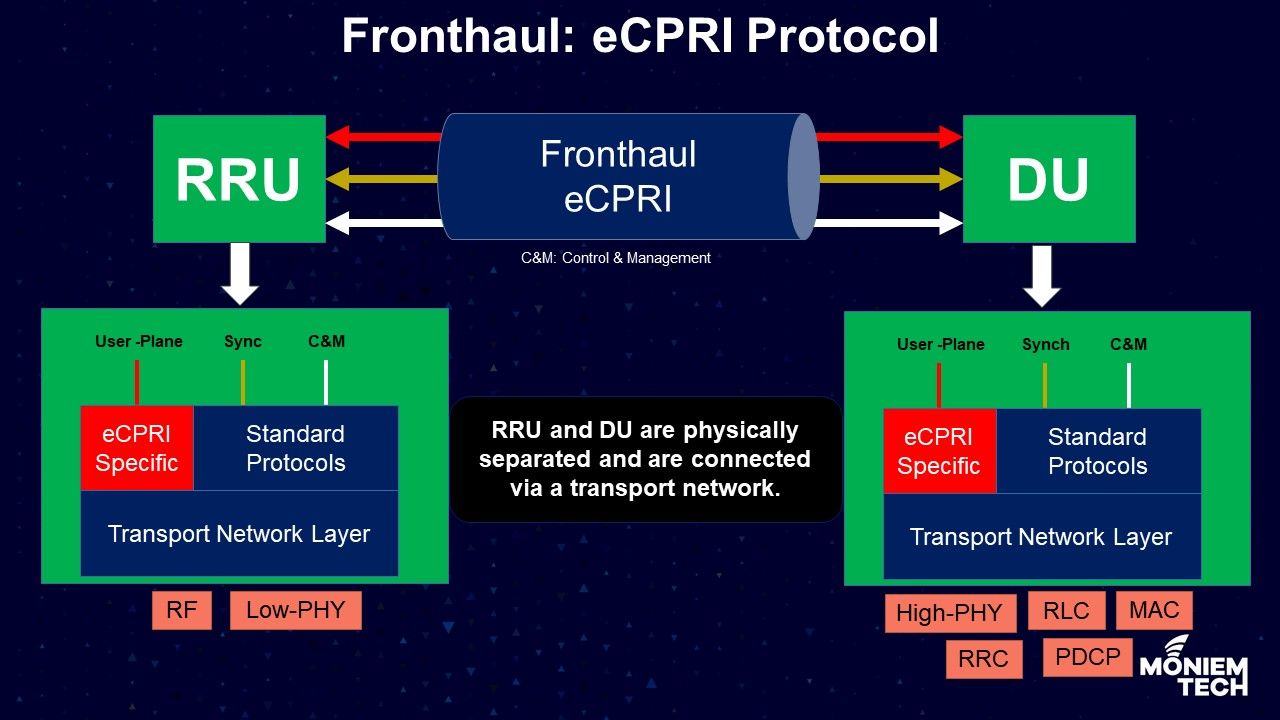
As I received many messages during the last week about the eCPRI topic in 5G and OpenRAN, I prepared some notes about this. eCPRI is replacing the CPRI protocol in 5G to reduce […]
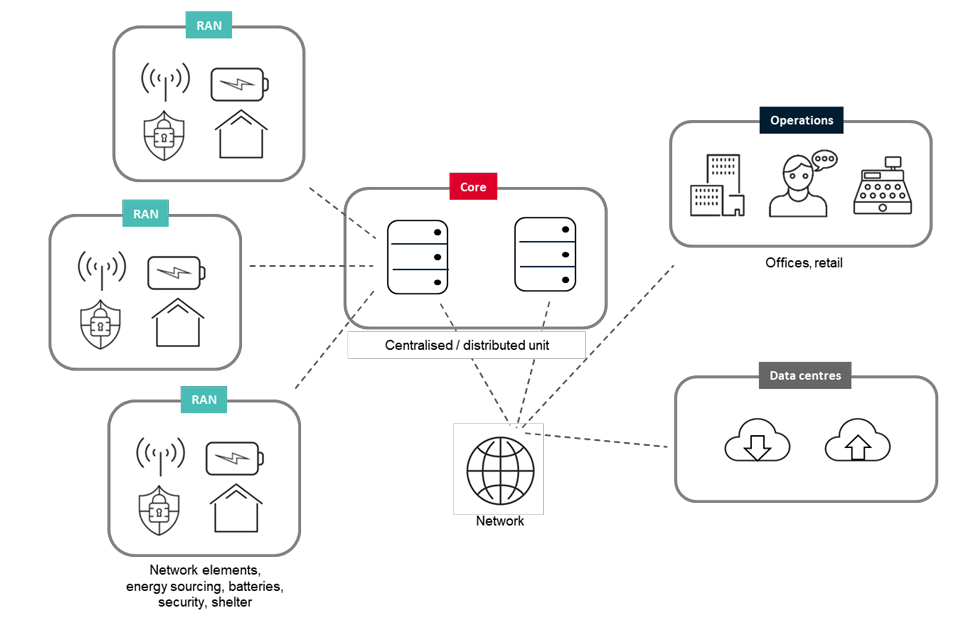
There’re many factors that impact the energy consumption in the mobile network operators, some of them related to climate, population density, and data consumption levels, while others are related to […]
Security is a driving factor in how 5G networks are built and operated – every element of a 5G network is required to have security controls in place for the […]
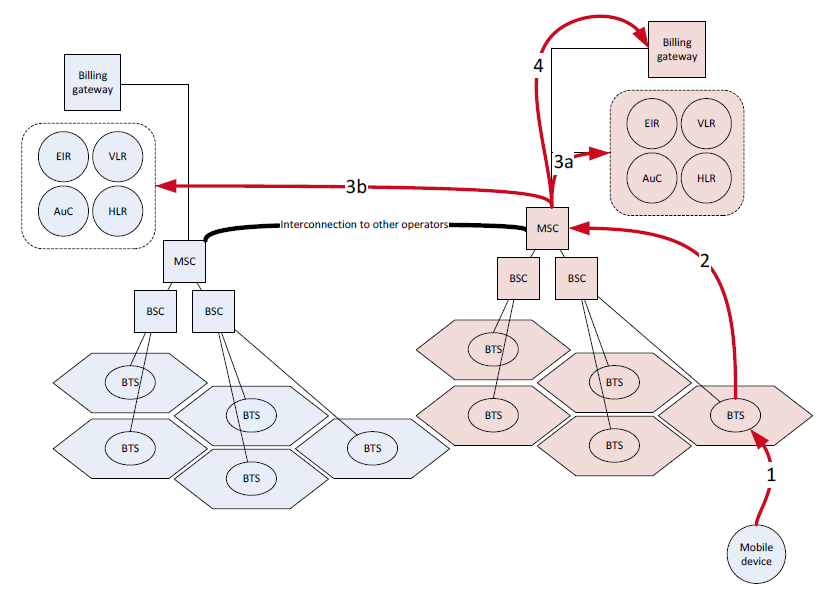
Recently, I received many questions and inquiries about the meaning of Roaming and some interesting questions: What is Roaming? What is the difference between National Roaming and International Roaming? First, […]

RAN (Radio Access Network) is the main telecommunication network component that is located between the core network and users’ equipment (such as a mobile phone). RAN is constituted of a […]
